Gallbladder Surgery
Gallbladder surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile. Bile helps in digesting fats, but when gallbladder function is impaired due to gallstones, inflammation, or infection, removal becomes necessary to prevent further complications.
When gallbladder function is impaired due to gallstones (cholelithiasis), inflammation (cholecystitis), infection, or bile duct obstruction, removal becomes necessary to prevent severe complications such as persistent pain, digestive issues, pancreatitis, or even rupture. Gallbladder disease can cause symptoms like nausea, bloating, indigestion, and sharp abdominal pain, often triggered after consuming fatty foods.
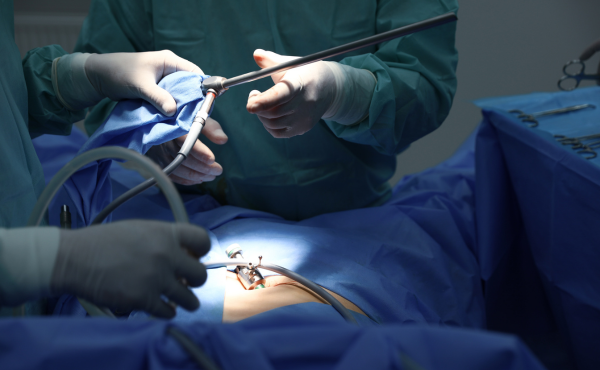
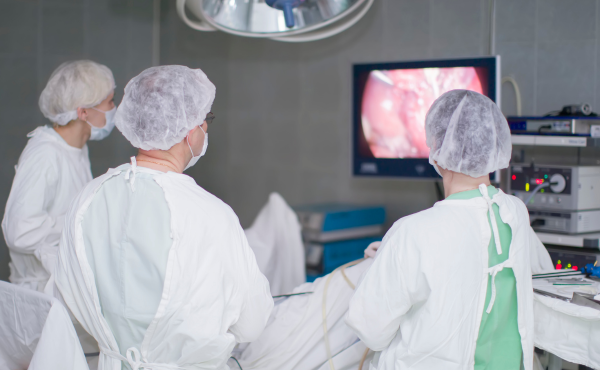
Why is Gallbladder Surgery Performed?
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) – Hardened deposits of bile that form in the gallbladder, leading to pain, inflammation, and digestive issues.
- Gallbladder Inflammation (Cholecystitis) – A condition where the gallbladder becomes swollen and infected, causing severe abdominal pain, fever, and nausea.
- Biliary Colic – Intense, intermittent pain caused by gallstones temporarily blocking the bile ducts.
- Bile Duct Obstruction – When gallstones or sludge block the flow of bile, leading to jaundice, infection, and liver damage.
- Gallbladder Polyps – Abnormal growths inside the gallbladder that may become cancerous over time.
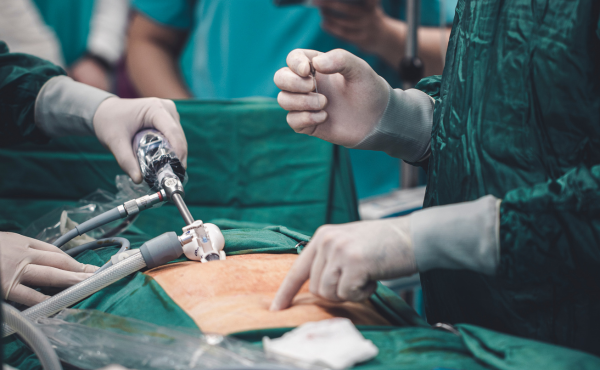
Types of Gallbladder Surgery :
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Minimally Invasive) : The most common and preferred method for gallbladder removal. Small incisions are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is used to guide the surgery.
- Open Cholecystectomy (Traditional Surgery) : Recommended for patients with severe gallbladder disease, infection, scarring, or complications from previous surgeries. A larger incision is made in the abdomen to access and remove the gallbladder.
- Single-Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (SILC) :A newer, advanced technique where the gallbladder is removed through a single incision, usually at the belly button. Requires specialized surgical expertise and is not suitable for all patients.
- Robotic-Assisted Cholecystectomy : Performed using robotic technology for enhanced precision and control. Provides a highly magnified 3D view, allowing for greater accuracy in delicate surgeries.
Recovery After Gallbladder Surgery
- Hospital Stay & Immediate Post-Surgery Care : Laparoscopic Surgery: Most patients can go home the same day or within 24 hours. Open Surgery: Requires a hospital stay of 2 to 5 days for monitoring and pain management.
- Pain Management : Pain and discomfort are common after surgery, but can be managed with prescribed medications and rest. Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications help manage discomfort.
- Obstruction of the Intestine – If the hernia blocks the passage of food or stool, leading to nausea, vomiting, bloating, or constipation, surgery is necessary to restore normal digestion.
- Strangulation Risk – If the herniated tissue becomes trapped and loses its blood supply, it can lead to tissue death (gangrene), which is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgery.