Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery is a procedure to repair a hernia, a condition where an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias commonly occur in the abdomen, groin, or diaphragm and can cause pain, discomfort, and complications if left untreated. Surgery is often recommended to prevent further complications such as strangulation, where the herniated tissue loses its blood supply, leading to severe pain, infection, or tissue death.
Hernia surgery can be performed using traditional open surgery, laparoscopic techniques, or robotic-assisted procedures, depending on the size, location, and complexity of the hernia. The goal of the surgery is to reposition the herniated tissue, reinforce the weakened muscle wall, and prevent recurrence using stitches or a surgical mesh.
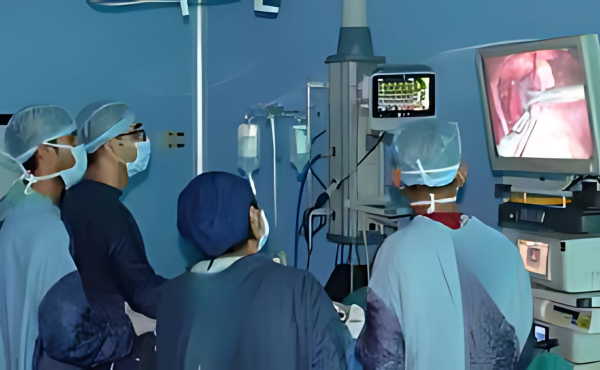
Types of Hernia Surgery :
- Open Hernia Repair (Herniorrhaphy or Hernioplasty) :
- A traditional surgical method where a single incision is made over the hernia site.
- The protruding tissue is pushed back into place, and the weakened muscle area is stitched or reinforced with a synthetic mesh (hernioplasty).
- Commonly used for large or complex hernias.
-
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair :
- A minimally invasive approach where small incisions are made, and a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) is inserted for visualization.
- Specialized instruments are used to repair the hernia and place a surgical mesh for reinforcement.
- Benefits include faster recovery, less pain, and reduced scarring.
-
Robotic Hernia Repair :
- Similar to laparoscopic surgery but performed with robotic-assisted technology for enhanced precision.
- The surgeon controls robotic arms from a console, allowing for delicate movements and better visualization.
- Recommended for complex or recurrent hernias.
Common Types of Hernias Treated with Surgery :
- Inguinal Hernia: Occurs in the groin area when the intestines push through a weak spot in the abdominal wall.
- Umbilical Hernia: Forms around the belly button due to weakness in the abdominal muscles.
- Incisional Hernia: Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision where the muscles have weakened.
- Femoral Hernia: Appears in the upper thigh near the groin, more common in women.
- Hiatal Hernia: Occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
- Hiatal Hernia – Occurs when the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, leading to acid reflux and digestive discomfort.
When is Hernia Surgery Needed?
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort – If the hernia causes ongoing pain, pressure, or discomfort that affects daily activities, surgery is often recommended.
- Increase in Size – A hernia that grows larger over time may indicate weakening of the abdominal wall, requiring surgical repair before complications arise.
- Obstruction of the Intestine – If the hernia blocks the passage of food or stool, leading to nausea, vomiting, bloating, or constipation, surgery is necessary to restore normal digestion.
- Strangulation Risk – If the herniated tissue becomes trapped and loses its blood supply, it can lead to tissue death (gangrene), which is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgery.
- Difficulty in Daily Activities – When a hernia interferes with routine activities like bending, lifting, or even walking