Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, is an advanced surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments to perform procedures with greater precision and minimal trauma to the body. A laparoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a high-definition camera and light source, provides a magnified and detailed view of the internal organs, allowing surgeons to operate with enhanced accuracy and control.
This technique is widely used for various abdominal and pelvic surgeries, reducing the need for large incisions and significantly improving patient outcomes. Laparoscopic surgery is associated with reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and a lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgery. It is commonly used for procedures such as gallbladder removal, hernia repair, appendectomy, and gastrointestinal surgeries.
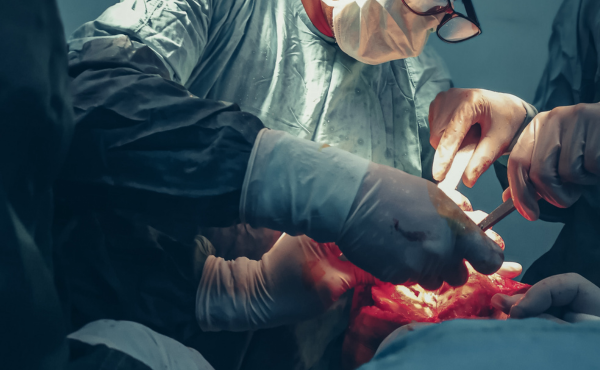
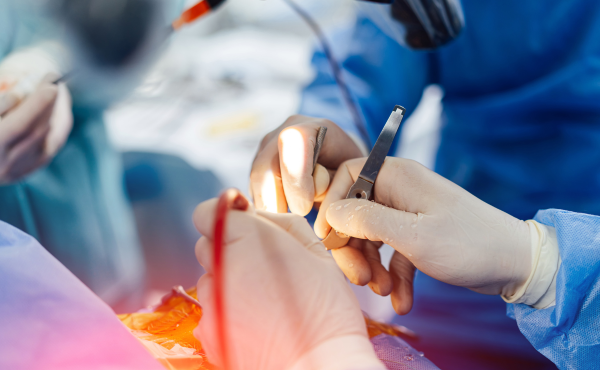
Causes of Conditions Requiring Laparoscopic Surgery :
- Gallbladder Disease (Gallstones, Cholecystitis) – High cholesterol or bilirubin levels can lead to gallstone formation, causing inflammation and blockage in the gallbladder. Obesity, rapid weight loss, liver disease, and genetic predisposition also increase the risk.Genetics – Inherited traits like misaligned teeth, jaw discrepancies, or overcrowding.
- Appendicitis – A blockage in the appendix caused by stool, infection, or a foreign body leads to inflammation and infection. Bacterial overgrowth and genetic susceptibility may also play a role.
- Gynecological Conditions (Endometriosis, Ovarian Cysts, Fibroids) – Hormonal imbalances, genetic factors, and chronic pelvic infections can contribute to abnormal tissue growth and cyst formation, often requiring laparoscopic procedures for treatment.
- Cancerous Growths (Colorectal, Uterine, Stomach Cancer, etc.) – Genetic mutations, lifestyle choices such as smoking and poor diet, and chronic inflammatory diseases increase the risk of cancerous tumors, which may require laparoscopic removal for treatment and staging.
Symptoms of Conditions Requiring Laparoscopic Surgery :
- Severe Abdominal Pain – Sharp or cramping pain in the upper right abdomen, especially after fatty meals.
- Visible Bulge or Lump – A noticeable swelling in the abdomen or groin that may enlarge when coughing or straining.
- Pain or Discomfort – Aching or burning sensation, especially when lifting heavy objects or standing for long periods.
- Severe Lower Right Abdominal Pain – Sudden, sharp pain that worsens with movement.
- Chronic Abdominal Pain – Persistent cramps or sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
- Persistent Indigestion or Swallowing Difficulties – Symptoms often associated with stomach or esophageal cancer.
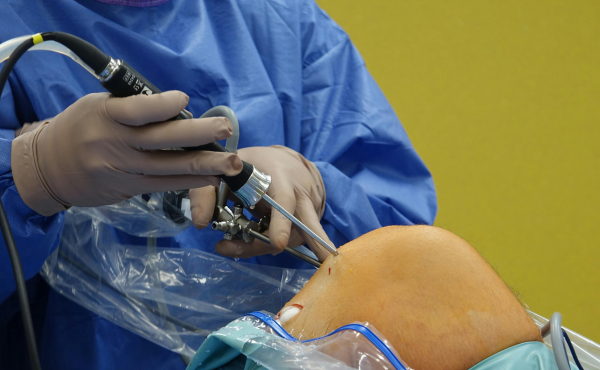
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery :
- Smaller Incisions – Uses tiny keyhole incisions instead of large cuts, leading to less scarring and faster recovery.
- Reduced Pain and Discomfort – Minimally invasive techniques cause less tissue trauma, resulting in less post-operative pain.
- Faster Recovery Time – Patients typically experience a quicker return to daily activities compared to traditional open surgery.
- Lower Risk of Infection – Smaller incisions reduce exposure to external contaminants, minimizing infection risks.
- Less Blood Loss – Precision instruments help control bleeding, reducing the need for blood transfusions.
- Enhanced Surgical Precision – High-definition cameras provide magnified views of internal organs, allowing for greater accuracy.